Chelation is a chemical combination with a metal in complexes in which the
metal is part of a ring. Organic ligand is called chelator or chelating agent,
the chelate is a metal complex. The larger number of ring closures to a metal
atom is the more stable the compound. This phenomenon is called the chelate
effect; it is generally attributed to an increase in the thermodynamic quantity
called entropy that accompanies chelation. The stability of a chelate is also
related to the number of atoms in the chelate ring. Monodentate ligands which
have one coordinating atom like H2O or NH3 are easily broken apart by other
chemical processes, whereas polydentate chelators, donating multiple binds to
metal ion, provide more stable complexes. Chlorophyll, green plant pigment, is a
chelate that consists of a central magnesium atom joined with four complex
chelating agent (pyrrole ring). The molecular structure of the chlorophyll is
similar to that of the heme bound to proteins to form hemoglobin, except that
the latter contains iron(II) ion in the center of the porphyrin. Heme is an iron
chelate. Chelation is applied in metal complex chemistry, organic and inorganic
chemistry, biochemistry, and environment protection. It is used in
chemotherapeutic treatments for metal poisoning. Chelating agents offers a wide
range of sequestrants to control metal ions in aqueous systems. By forming
stable water soluble complexes with multivalent metal ions, chelating agents
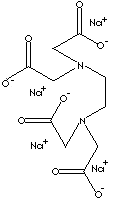
prevent undesired interaction by blocking normal reactivity of metal ions. EDTA,
ethylenediaminetetraacetate (hexadentating), is a good example of common
chelating agent which have nitrogen atoms and short chain carboxylic groups. The
sodium salt of EDTA is used as an antidote for metal poisoning, an
anticoagulant, and an ingredient in a variety of detergents. Chelating agents
are important in the field of soap, detergents, textile dyeing, water softening,
metal finishing and plating, pulp and paper, enzyme deactivation, photo
chemistry, and bacteriocides.
|